Common Name: white leadtree
Family: Fabaceae
Common Synonyms: none
USDA Hardiness Zone: 9a-11
Growth Habit: Shrub to small tree
Origin: Mexico and Central America
FISC Category: 2
FDACS Listed Noxious Weed: Yes
Introduction Date: Introduced first to Hawaii in 1864 and soon afterwards to the mainland United States in Florida and Texas
IFAS Assessment:
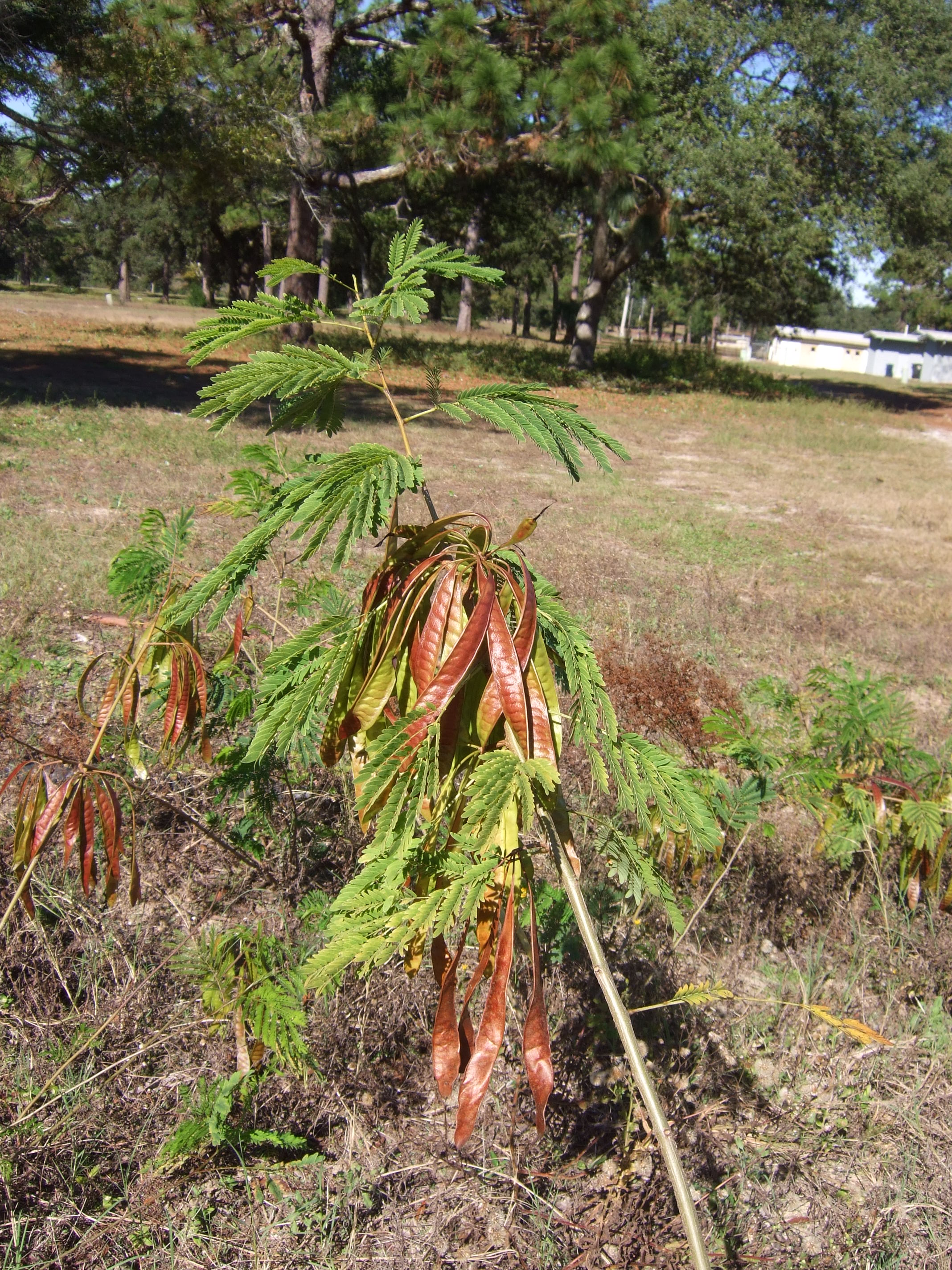

Shrub or small tree growing up to 7.5 m tall. Leaves up to 25 cm long, twice divided with 12 sets of opposite arranged lance-shaped leaflets. Flowers are clustered at tips of branches, and are white. Fruits are flat, brown pods 10 to 15 cm long with up to 20 shiny brown seeds.
Ruderal, coastal strands, disturbed areas
Prolific seed producer. Seeds spread by rodents and birds. Rapidly re-sprouts post-fire and produces new shoots when cut. Difficult to control, chemical treatments often not wholly effective. Treated plants can stay dormant for long periods. Creates long-lived seed bank.
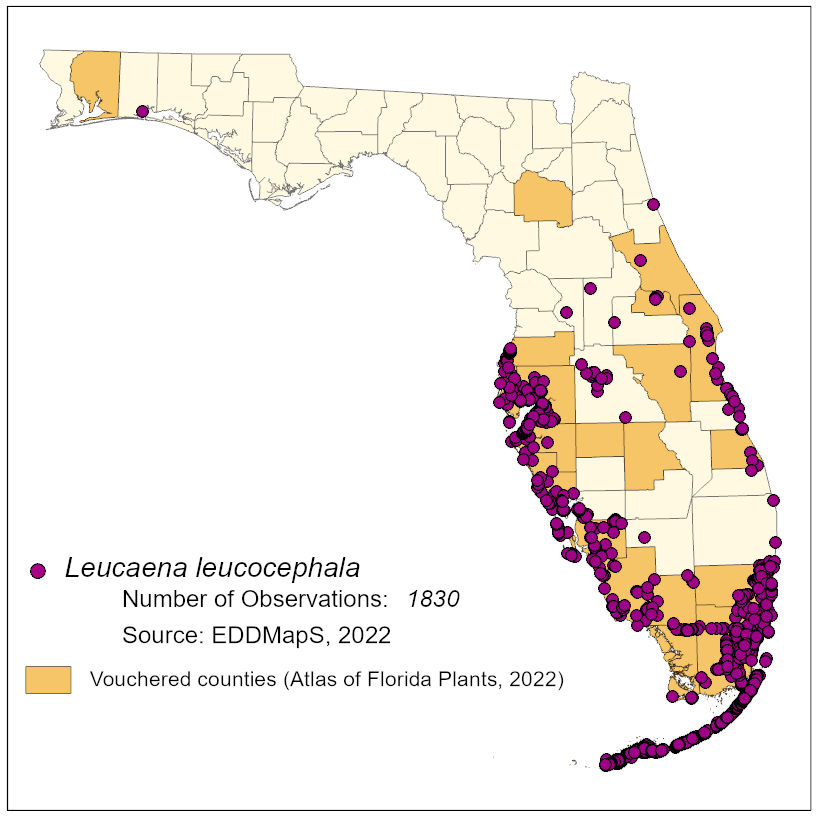
Remove all plants prior to seed production. Difficult to control and variable results have been reported. Must track treated individuals for many months to ensure complete kill vs. top kill with dormancy.
Texas invasives database. 2017. Leucaena leucocephala. http://www.texasinvasives.org/plant_database/detail.php?symbol=LELE10/Accessed September 19, 2017.
IFAS, UF. 2017. Assessment of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas. Leucaena leucocephala . https://assessment.ifas.ufl.edu/assessments/leucaena-leucocephala/Accessed September 19, 2017.
IFAS, Center for Aquatic and Invasive Plants. 2017. Leucaena leucocephala. http://plants.ifas.ufl.edu/plant-directory/leucaena-leucocephala/Accessed September 19, 2017.
Dave's Garden. 2017. PlantFiles: white leadtree (Leucaena leucocephala) . http://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/64328/Accessed September 19, 2017.