Common Name: rubber vine
Family: Apocynaceae
Common Synonyms: none
USDA Hardiness Zone: 10a-11
Growth Habit: Vine
Origin: Madagascar
FISC Category: 2
FDACS Listed Noxious Weed: No
Introduction Date: pre-1904
IFAS Assessment:
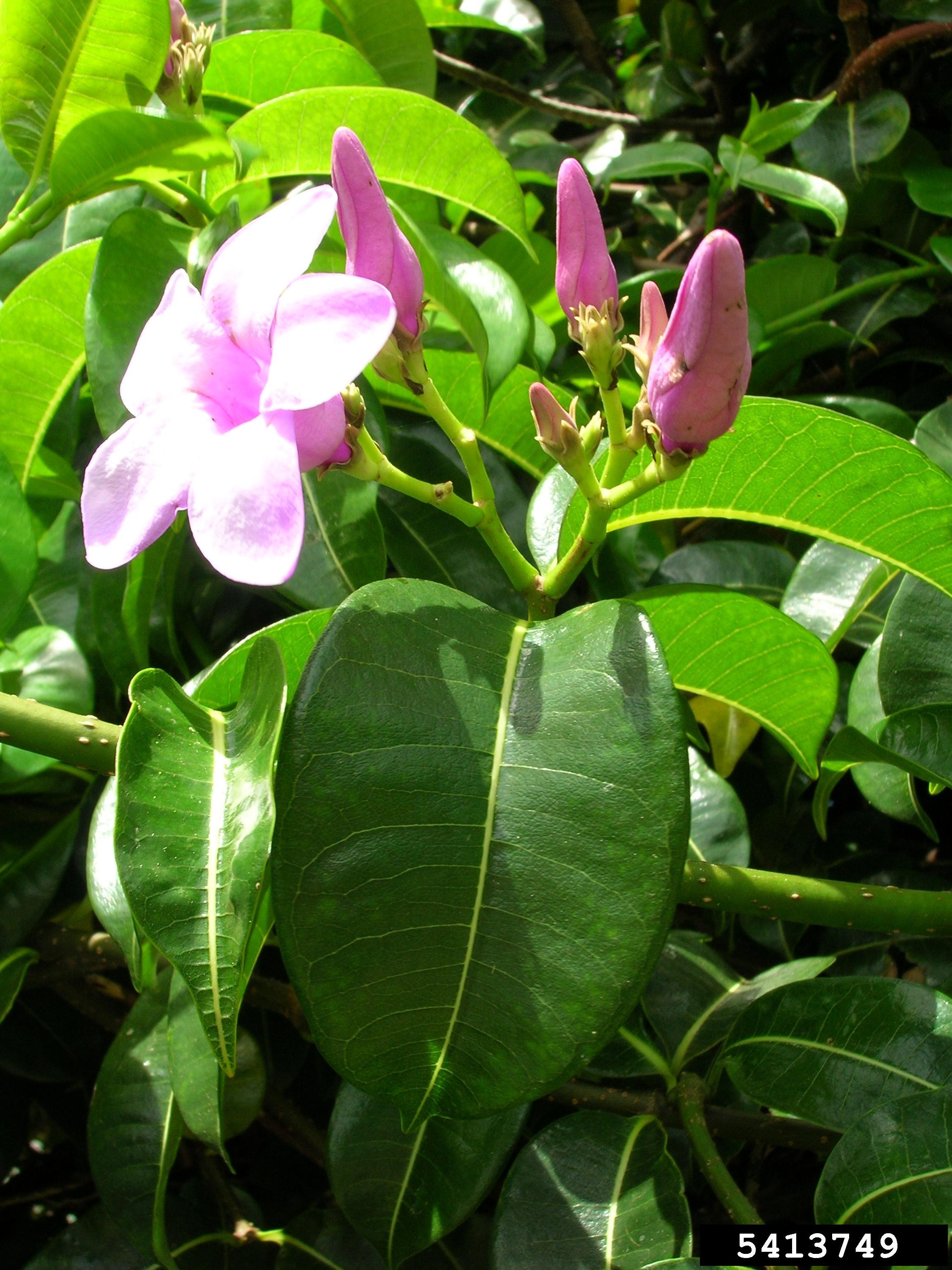

Woody vine or vining shrub with milky sap, stem dotted with lenticels. Leaves opposite, ovate, dark glossy green to 9 cm long and 5 cm wide with entire margins and round bases. Showy flowers to 4 cm long and 6 cm wide in terminal clusters of 1-4, pale purple to reddish purple, funnel shaped. Fruit a woody angled brown pod to 8 cm long, which splits at maturity to expose seeds with white silky hairs.
Mangrove swamp, hammock, shell mound, rockland hammock
Seeds are wind and water dispersed.
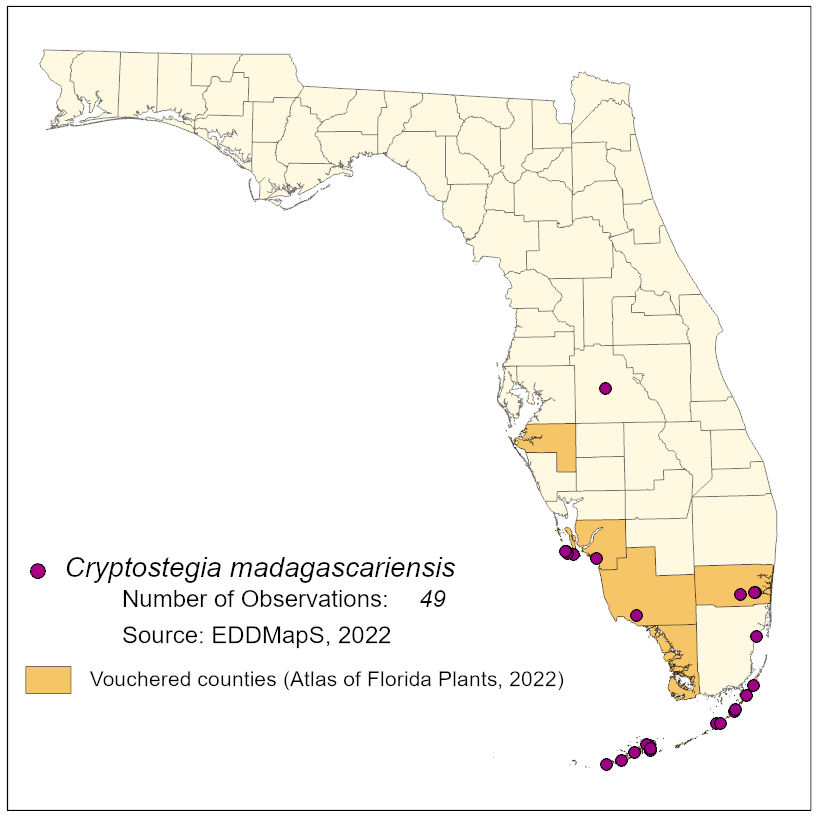
Note: The milky sap is toxic and therefore hand-pulling should be done carefully (Starr et al.)
Dave's Garden. 2014. PlantFiles: Madagascar Rubbervine, Cryptostegia madagascariensis. http://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/55532/. Accessed on June 20, 2014.
Langeland, K.A., H.M. Cherry, C.M. McCormick, K.C. Burks. 2008. Identification and Biology of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas-Second Edition. IFAS Publication SP 257. University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida.
Starr, F., K. Starr and L. Loope. 2003. Cryptostegia spp. Rubber vine, Ascepiadaceae. United States Geological Survey - Biological Resources Division, Haleakala Field Station, Maui, Hawaii.
Wunderlin, R. P., and B. F. Hansen. 2008. Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants (http://florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/).[S. M. Landry and K. N. Campbell (application development), Florida Center for Community Design and Research.] Institute for Systematic Botany, University of South Florida, Tampa.