Common Name: Chinese tallow
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Common Synonyms: Sapium sebiferum
USDA Hardiness Zone: 8a-11
Growth Habit: Tree
Origin: Southeastern Asia
FISC Category: 1
FDACS Listed Noxious Weed: Yes
Introduction Date: 1900s
IFAS Assessment:
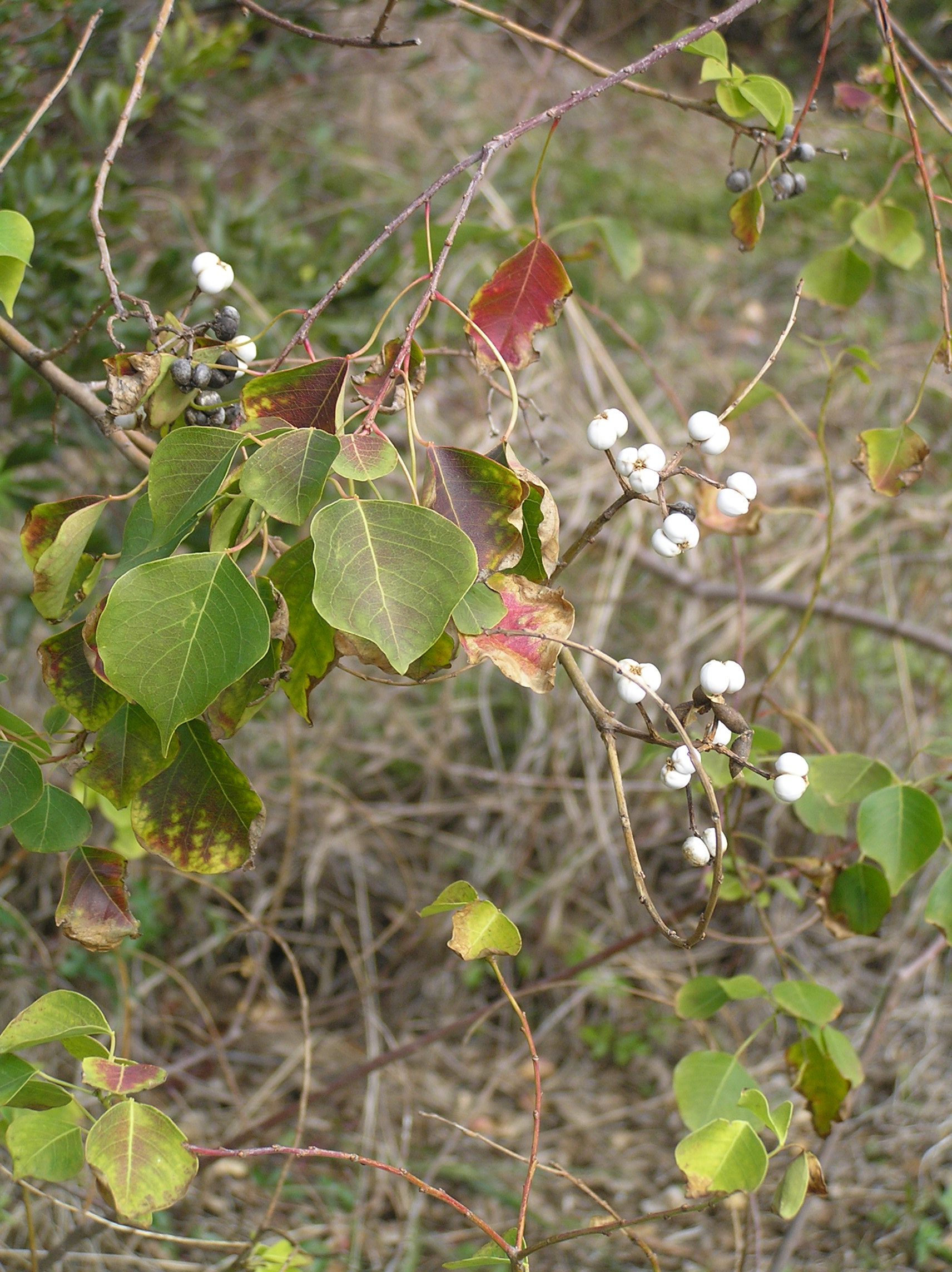


Deciduous tree 6-18 m tall. Sap milky. Leaves alternate, entire, rhombic to ovate, acuminate, 3-6 cm wide, petioles long and slender with 2 glands at the apex. Flowers small, yellow, apetalous, in spikes 10-20 cm long. Fruit a three-lobed capsule 1.3 cm wide, seeds 3, covered with a white waxy coating, ripening from August to November.
Swamps, floodplain forests, and mesic to scrubby flatwoods
Chinese tallow trees develop a strong, deep taproot. This enables young trees to withstand periods of drought. Seeds are spread by many species of birds, and moving water can also serve as a mechanism for seed dispersal.
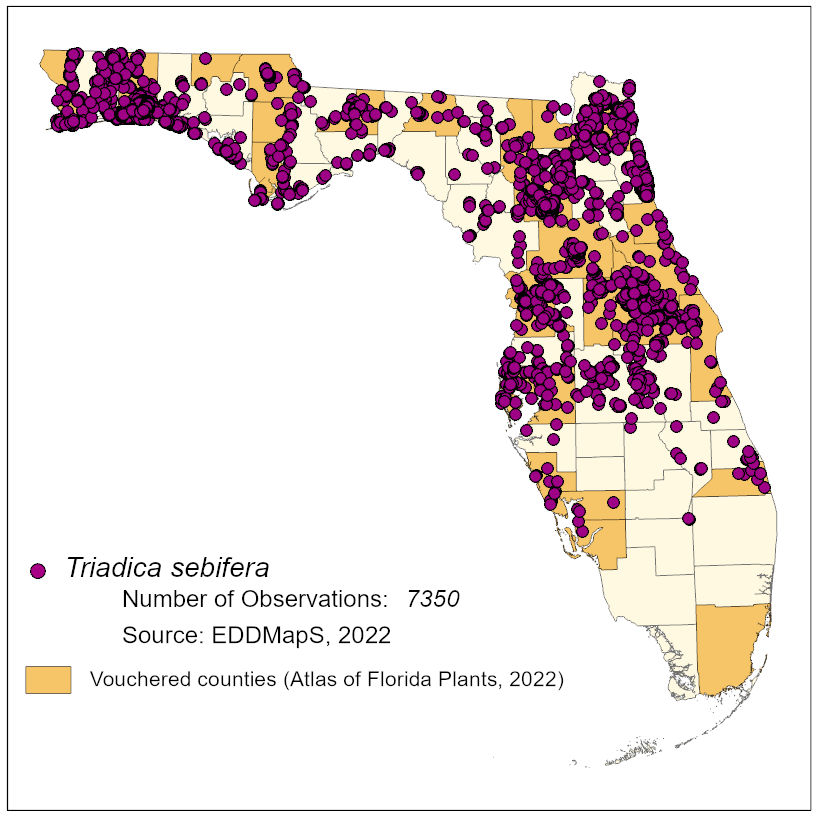
NA
Dave's Garden. 2014. PlantFiles: Chinese tallow tree, Triadica sebifera. http://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/32151/. Accessed on June 19, 2014.
Langeland, K.A., H.M. Cherry, C.M. McCormick, K.C. Burks. 2008. Identification and Biology of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas-Second Edition. IFAS Publication SP 257. University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida.
Langeland, K.A., J.A. Ferrell, B. Sellers, G.E. MacDonald, and R.K. Stocker. 2011. Integrated management of non-native plants in natural areas of Florida. EDIS publication SP 242. University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida.