Common Name: shoebutton ardisia
Family: Myrsinaceae
Common Synonyms: none
USDA Hardiness Zone: 9a-11
Growth Habit: Evergreen shrub or small tree
Origin: India, China, Southeast Asia
FISC Category: 1
FDACS Listed Noxious Weed: Yes
Introduction Date: around 1900
IFAS Assessment:
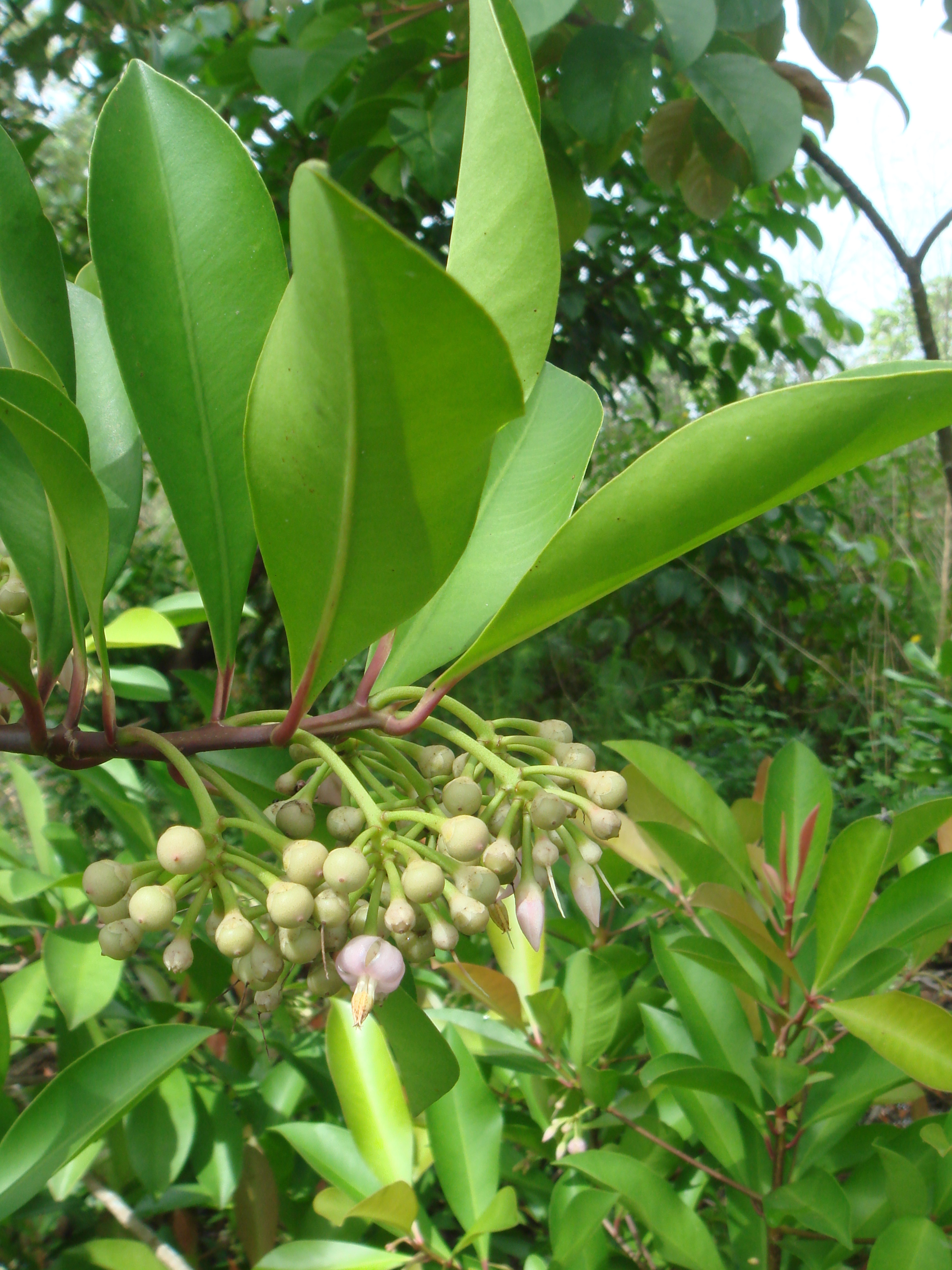
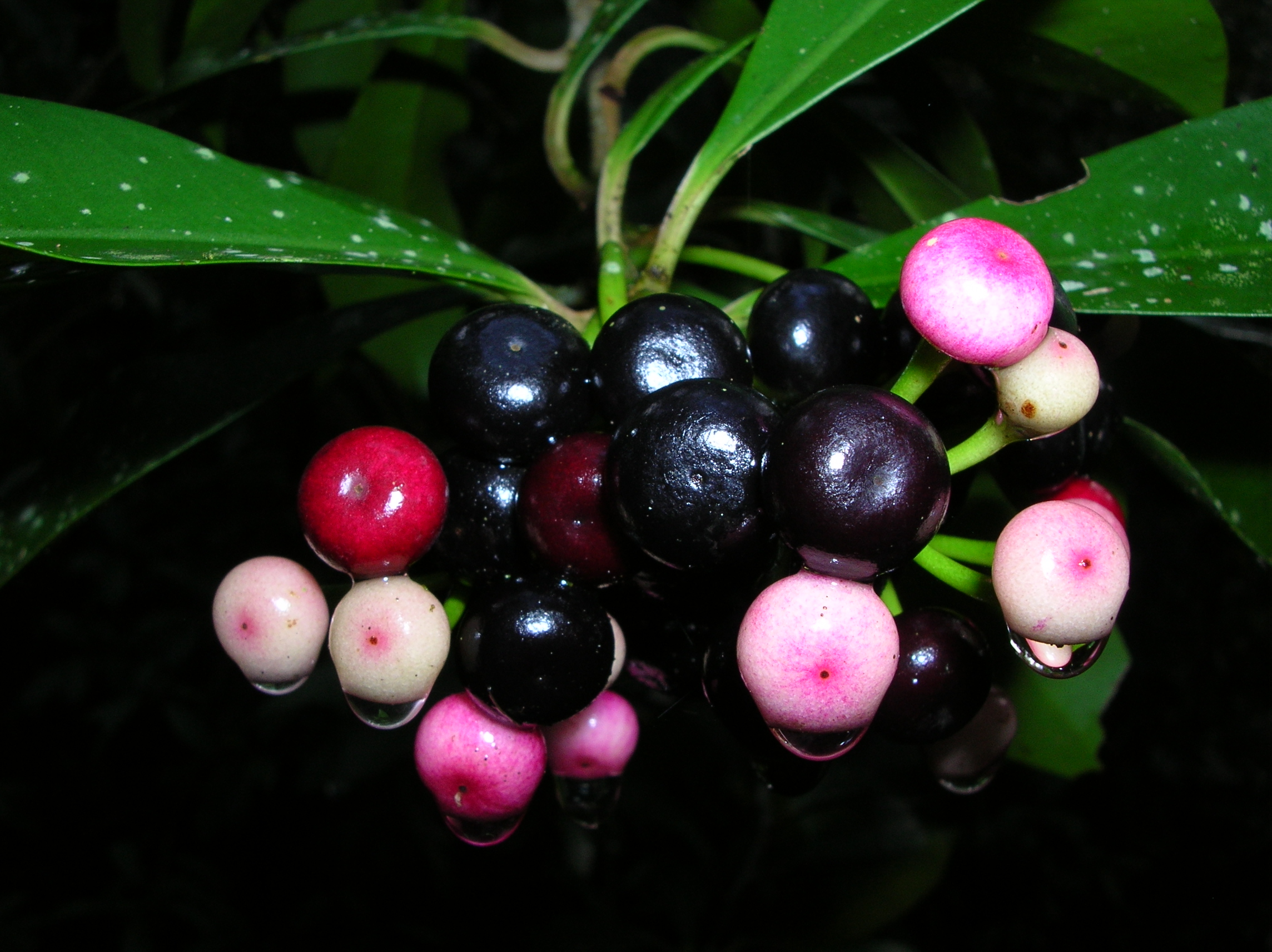


Evergreen shrub or small tree, to 5 m, glabrous. Leaves alternate, to 20 cm, oblong to oval shaped, entire margins, fleshy, new foliage reddish. Star-shaped flowers in axillary clusters, petals mauve colored. Fruit is a round drupe, red turning black when ripe with white flesh.
Coastal berm, maritime hammock, hardwood hammock, mesic flatwoods, strand swamp, cabbage palm hammock, disturbed areas
Prolific reproduction, bird dispersed. Similar to the native marlberry (Ardisia escallonioides) or myrsine (Rapanea punctata) but is larger with conspicuous axillary clusters of mauve flowers.
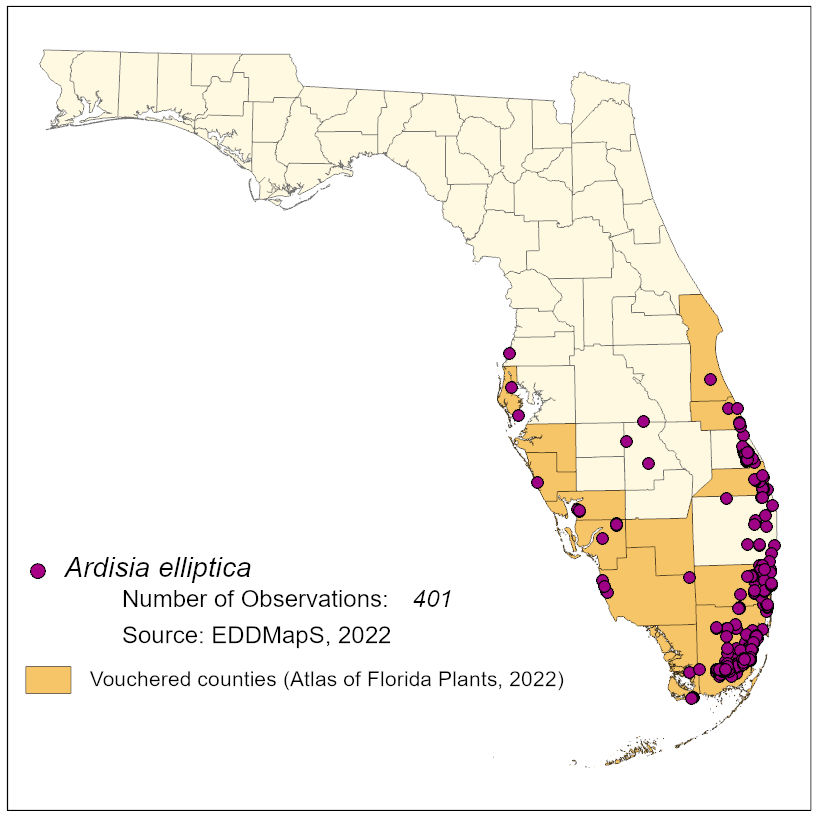
NA
Dave's Garden. 2014. PlantFiles: Shoebutton Ardisia, Ardisia elliptica. http://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/go/31889/. Accessed on June 20, 2014.
Langeland, K.A., H.M. Cherry, C.M. McCormick, K.C. Burks. 2008. Identification and Biology of Non-Native Plants in Florida's Natural Areas-Second Edition. IFAS Publication SP 257. University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida.
Langeland, K.A., J.A. Ferrell, B. Sellers, G.E. MacDonald, and R.K. Stocker. 2011. Integrated management of non-native plants in natural areas of Florida. EDIS publication SP 242. University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida.
Wunderlin, R. P., and B. F. Hansen. 2008. Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants (http://florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/).[S. M. Landry and K. N. Campbell (application development), Florida Center for Community Design and Research.] Institute for Systematic Botany, University of South Florida, Tampa.